


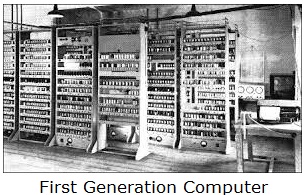
First Generation of Computers (1940s-1950s)
The main features of the first generation are:
- Main electronic component – vacuum tube
- Main memory – magnetic drums and magnetic tapes
- Programming language – machine language
- Power – consume a lot of electricity and generate a lot of heat.
- Speed and size – very slow and very large in size (often taking up entire room).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and paper tape.
- Examples – ENIAC, UNIVAC1, IBM 650, IBM 701,IBM 750 etc.
- Quantity – there were about 100 different vacuum tube computers produced between 1942 and1963.

Second Generation of Computers (1950s-1960s)
The main features of the second generation are :
- Main electronic component – transistor
- Memory – magnetic core and magnetic tape / disk
- Programming language – assembly language
- Power and size – low power consumption, generated less heat, and smaller in size (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the first generation computers).
- Input/output devices – punched cards and magnetic tape.
- Examples – IBM 1401, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107,CDC 1604, CDC 3600 etc.


Third Generation of Computers (1960s-1970s)
The main features of the third generation are :
- Main electronic component – integrated circuits (ICs)
- Memory – large magnetic core, magnetic tape / disk
- Programming language – high level language (FORTRAN, BASIC, Pascal, COBOL, C, etc.)
- Size – smaller, cheaper, and more efficient than second generation computers (they were called minicomputers).
- Speed – improvement of speed and reliability (in comparison with the second generation computers).
- Input / output devices – magnetic tape, keyboard, monitor, printer, etc.
- Examples – IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP-11, UNIVAC 1108,Honeywell-6000 series,TDC-316 etc.


Fourth Generation of Computers (1970s-1980s)
The main features of the fourth generation are :
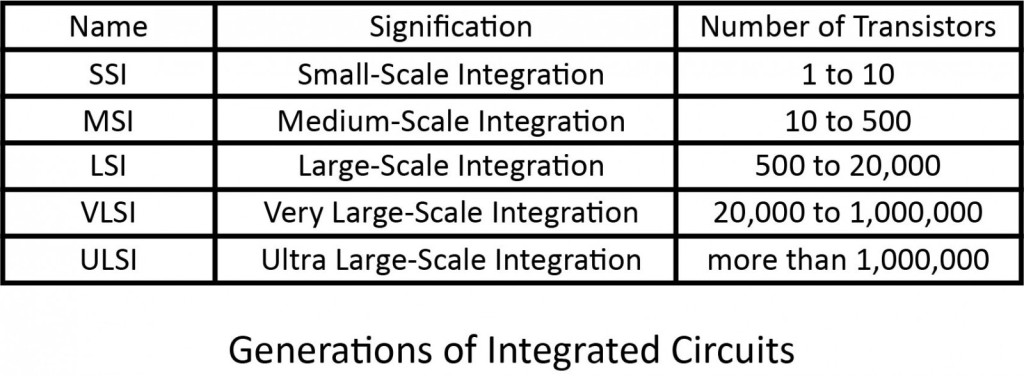
- Main electronic component – very large-scale integration (VLSI) and microprocessor.
-
VLSI– thousands of transistors on a single microchip.
- Memory – semiconductor memory (such as RAM, ROM, etc.)
- RAM (random-access memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporary stores of programs and data (volatile: its contents are lost when the computer is turned off).
- ROM (read-only memory) – a type of data storage used in computers that permanently stores data and programs (non-volatile: its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off).
- Programming language – high level language (Python, C#, Java, JavaScript, Rust etc.).
- A mix of both third- and fourth-generation languages
- Size – smaller, cheaper and more efficient than third generation computers.
- Speed – improvement of speed, accuracy, and reliability (in comparison with the third generation computers).
- Input / output devices – keyboard, pointing devices, optical scanning, monitor, printer, etc.
- Network – a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
- Examples – IBM PC, STAR 1000, APPLE II, Apple Macintosh, etc.


Fifth Generation of Computers (1980s-Present)
The main features of the fifth generation are :
- Main electronic component: based on artificial intelligence (AI), uses the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method.
- ULSI – millions of transistors on a single microchip
- Parallel processing method – use two or more microprocessors to run tasks simultaneously.
- Language – understand natural language (human language).
- Power – consume less power and generate less heat.
- Speed – remarkable improvement of speed, accuracy and reliability (in comparison with the fourth generation computers).
- Size – portable and small in size, and have a huge storage capacity.
- Input / output device – keyboard, monitor, mouse, trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognize voice / speech), light scanner, printer, etc.
- Example – desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones, etc.





Leave a comment